本篇介绍Pytorch的两个高阶操作: where与gather。
where
使用
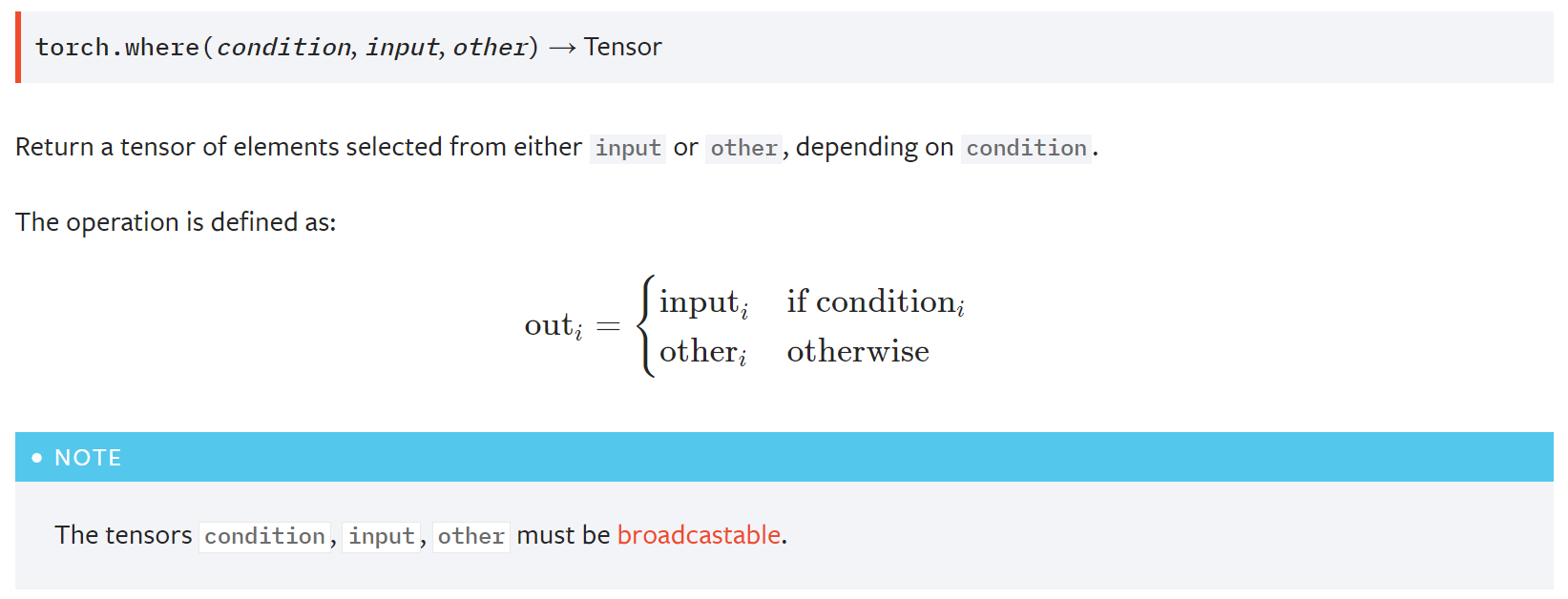
图片来自 Pytorch官方文档.
- 就像python中的三元运算一样,如果条件满足,选input的元素,不满足选other的元素。
1 | In[49]: cond = torch.rand(2,2) # 制作一个选择器 |
为什么会有where
- 以前我们通常在for循环下以 c[0] = a[0] 来进行整段的复制,但是这些都是在cpu上完成的,想要用gpu并行,就必须摆脱这种方式。
- 使用where语句,在gpu中,高度并行。
- cond 可以由cpu生成也可以有gpu生成。
gather
1 | torch.gather(input, dim, index, out=None, sparse_grad=False) → Tensor |
收集/查表
input 理解为一张表;dim决定哪个维度查找;所查的索引
这样做一来可以用gpu加速,二来可以达到从 relative gather 到 global gather。
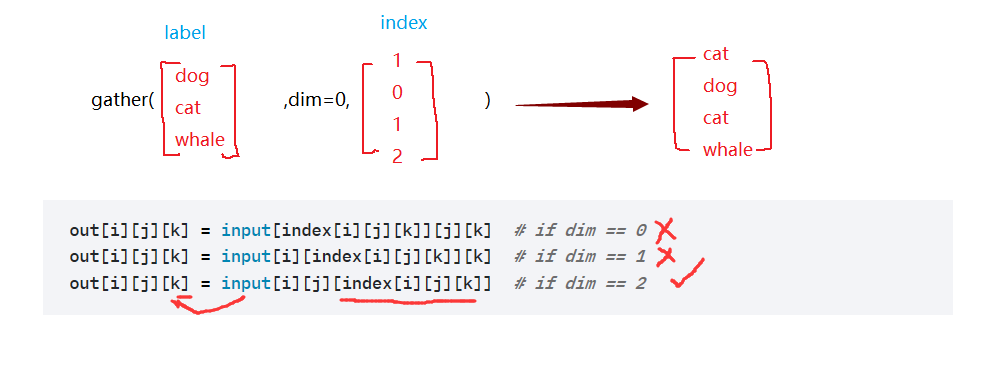
例子:
以手写体数字为例,我们假设输出[4,10]
每张图片取可能性最大的前3
1 | In[3]: prob=torch.randn(4,10) |

